
Insulation protection requirements for power adapters

1. Insulation type
Insulation materials and insulation protection must be used to ensure the normal operation of the circuit and when there is a voltage higher than the dangerous voltage inside the circuit. UL60950 divides insulation into five categories: functional insulation, basic insulation, additional insulation, double insulation, and reinforced insulation.
① Functional insulation: It is a necessary insulation for the correct operation of equipment, does not provide electric shock safety protection, but can reduce ignition and combustion. For example, the paint of enameled wire.
② Basic insulation: The most basic insulation to avoid electric shock. Relying solely on basic insulation is not safe, and safety requirements must be achieved through additional insulation and secondary protection of protective grounding, such as interlayer insulation of coils.
③ Additional insulation: Insulation independently added to the basic insulation to ensure secondary protection against electric shock in the event of accidental failure of the basic insulation. The minimum thickness of the additional insulation single-layer material must be greater than or equal to 0.4mm.
④ Double insulation: composed of a combination of basic insulation and additional insulation, it is a secondary insulation system.
⑤ Enhanced insulation: A single insulation system that prevents electric shock, equivalent to double insulation. The minimum thickness of the single layer used inside is greater than or equal to 0.4mm. There may be several layers, but each layer cannot be tested separately.
2. Equipment level and insulation requirements
Different types of circuits require different types of insulation:
① Class I equipment. This type of equipment adopts protective grounding, that is, the metal chassis is grounded to a protective ground as Level 1 protection. Only basic insulation is required between any hazardous voltage components and the chassis, such as station communication power supplies.
② Class II equipment. Using double insulation and reinforced insulation, without metal casing and grounding screws, such as portable chargers.
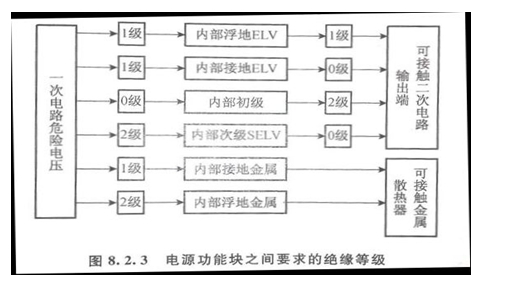
③ Class III equipment. Powered by the SELV source and a power source with no potential hazardous voltage internally, only basic insulation is required, such as circuit board power supply. Figure 8.2.3 shows a simple functional block diagram of the power supply. From the diagram, first distinguish whether the internal circuit functional blocks are LCC, SELV, TNV, ELV, or hazardous voltage.
Then determine the insulation level and quantity between functional blocks and internal components used. From the diagram, it can be seen that at least two poles of insulation are required between the hazardous voltage and the parts that the user can come into contact with.
For example, the ELV path of a floating ground must have two poles insulated, and there must be at least one level between the ELV and the user, otherwise the ELV circuit will be unsafe if a single level fails. However, if the ELV circuit is grounded for protection (providing level 1 protection), only adding level 1 is sufficient. Similar situations such as heat sinks and metal casings must be isolated from hazardous voltages using Level 2 insulation. Level 1 can only be used if the metal is grounded.
3. Insulation materials
Solid insulation materials should be selected based on working voltage, electrical strength, temperature requirements, mechanical strength, and working environment, and these materials should be moisture resistant and flame retardant; If it is wire insulation material, the flexibility of the material is also required.
Semiconductor devices and other components are molded into solid insulation materials, and their insulation is individually evaluated and tested for quality during the factory manufacturing process. The film, tape, and sheet of solid insulation materials have thickness requirements: if single-layer insulation is used, the minimum thickness is greater than or equal to 0.4mm; If it is a two-layer insulation, there is no thickness requirement, but each layer must meet the electrical strength requirements; If it is three or more layers, there is no minimum thickness requirement, but every combination of two layers must meet the corresponding electrical strength requirements. There is no thickness requirement for basic insulation or functional insulation.