With the continuous progress of technology and the increasing demand for electricity, the types and functions of power converters are also constantly enriched and improved. How should we choose from the complex and diverse types of power converters in the market? This article will provide a detailed introduction to the classification and selection techniques of power converters, hoping to provide assistance in your selection of power converters!
ClassificationBy energy type
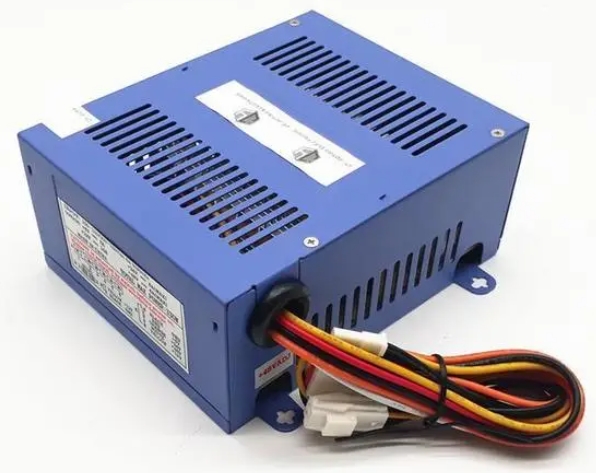 (1) Communication to communication
(1) Communication to communicationAn AC to AC converter is a device that converts an AC power source into another AC power source. This type of converter is commonly used to adjust voltage, frequency, or phase to meet the needs of different devices or systems, and is widely used in industries, energy, transportation, and other fields.
(2) AC to DCAC-DC converter is a device that converts AC power into DC power. Its main function is to convert unstable AC power into stable DC power to meet the working needs of various electronic devices. It has a wide range of applications in fields such as home, industry, communication, and energy.
(3) DC to DCA direct current to direct current (DC-DC) converter is a device that converts a DC power source into another DC power source. It is mainly used to adjust the power supply voltage, provide isolation, eliminate noise, and improve efficiency. This type of converter has been widely used in modern electronic devices.
(4) DC to ACA direct current to alternating current (DC-AC) converter, also known as an inverter, is a device that converts direct current power into alternating current power. It is typically used to convert direct current power from batteries, solar panels, and other sources into alternating current power for use in household, industrial, or commercial electrical equipment.
By purpose
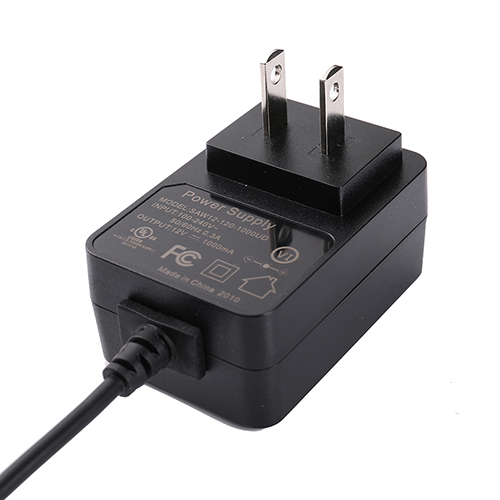 (1) Conversion plug
(1) Conversion plugThe power conversion plug is mainly used to convert one type of power plug into another, so as to use appliances in different countries and regions. This type of plug is only used for the transfer between plugs or between plugs and sockets, and has no voltage transformation function. Therefore, when using appliances in different countries, a power conversion plug is essential.
(2) InverterAn inverter is a device that converts direct current into alternating current. It is usually used to convert direct current sources such as batteries and solar panels into alternating current sources for use in household, industrial, or commercial electrical equipment. However, it should be noted that the selection should be based on the power and current requirements of the electrical appliances used to ensure that they can meet the usage needs of the appliances.
(3) TransformerA transformer is a static electrical device used to transform AC voltage and current and transmit AC electrical energy. It mainly achieves the transformation of voltage and current through the principle of electromagnetic induction to meet the requirements of different electrical appliances for power supply voltage and current.
Tips for purchasing power converters
 1. Determine requirements
1. Determine requirementsFirstly, clarify the type and specifications of power supply you need to convert, such as whether it is AC to DC or DC to AC, as well as the required input and output voltage, current, and power parameters.
(1) Communication to communicationThis type of converter is mainly used to adjust the voltage, frequency, or phase of AC power sources, or to convert between AC power sources of different voltages and frequencies. It is commonly used in industrial equipment, motor drives, power systems, aerospace and other fields, and is used to match equipment or systems with different voltage and frequency requirements.
(2) AC to DCThis type of converter is mainly used to convert AC power into DC power, usually including steps such as rectification, filtering, and voltage stabilization. It is widely used in consumer electronics, communication equipment, computers, household appliances, and other fields, providing stable and reliable DC power for these devices.
(3) DC to DCThis type of converter is mainly used to convert one DC power source to another DC power source, which may involve voltage increase, decrease, or transformation. It is commonly used in the fields of electric vehicles, mobile devices, aerospace, military equipment, etc., and is used to provide DC power sources that meet the needs of different equipment.
(4) DC to ACThis type of converter is mainly used to convert DC power into AC power, and is usually used in the inverter process, such as solar inverters, electric vehicle chargers, etc. It is commonly used in renewable energy systems (such as solar and wind energy), electric vehicle charging stations, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), etc., to convert DC power into AC power for use in the power grid or load.
2. Understanding QualityWhen choosing a power converter, it is important to choose products with reliable quality and good brand reputation. Product quality and reliability can be evaluated by reviewing product reviews, user feedback, and brand reputation.
3. Check security performancePower converters involve power conversion and usage, therefore safety performance is crucial. Ensure that the selected product has protection functions such as overcurrent, overvoltage, and overheating, and complies with relevant safety standards and certifications.
4. Looking at efficiency and energy consumptionThe efficiency and energy consumption of power converters are also factors that need to be considered. Efficient converters can reduce energy waste and heat generation, while low-energy converters contribute to energy conservation and emission reduction.
5. Check compatibilityEnsure that the interface of the selected power converter is compatible with your device and check if it supports the required plug type and socket standard.
Precautions for using power converters
 1. Safe operation
1. Safe operationWhen using a power converter, it is essential to follow safe operating procedures. Do not expose the converter to damp or high temperature environments to avoid hazards such as short circuits and fires.
2. Conduct a thorough inspectionBefore use, check if the wires and plugs of the power converter are intact and free from damage or looseness. Ensure that the plug is tightly connected to the socket to avoid poor contact or looseness that may cause power instability or interruption.
3. Avoid overloadDo not exceed the rated power of the power converter to avoid overload use. Overloading may cause equipment damage or lead to safety accidents such as fires.
4. Pay attention to groundingEnsure that the grounding terminal of the power converter is properly connected to provide safe grounding protection. Grounding can prevent dangerous situations such as insulation damage to electrical equipment or electric shock to personnel.
5. Regular maintenanceRegularly clean and maintain the power converter to ensure its normal operation and extend its service life. Clean up dust and debris, check the connection of wires and plugs, and replace damaged components in a timely manner.
summaryIn summary, when choosing a power converter, it is necessary to fully understand your own needs and equipment requirements, and choose a power converter with reliable performance, efficient conversion, and good safety. This will help improve the reliability of the equipment, extend its service life, and bring a better user experience.




